
.png)
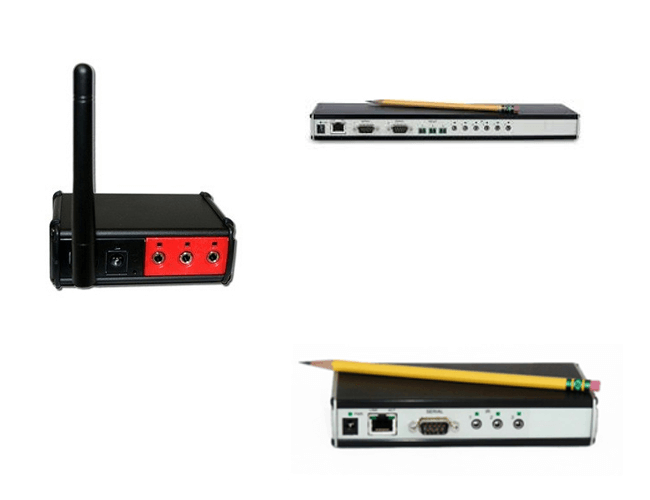
Global Caché
With Global Caché driver for ComfortClick bOS you can integrate and control any audio video device regardless of the manufacturer.
Global Caché
With Global Caché driver for ComfortClick bOS you can integrate and control any audio video device regardless of the manufacturer.
Global Cache network adapters receive command codes via LAN and send the IR signal to IR emitters attached to individual AV devices.
Global Cache driver is used to connect to GC-100 and iTach adapters. Driver can send IR codes, control relay outputs and monitors digital inputs. Controlling the RS-232 ports on GC devices is currently not supported (RS-232 can only be used to connect the GC-IRL device for IR code learning).
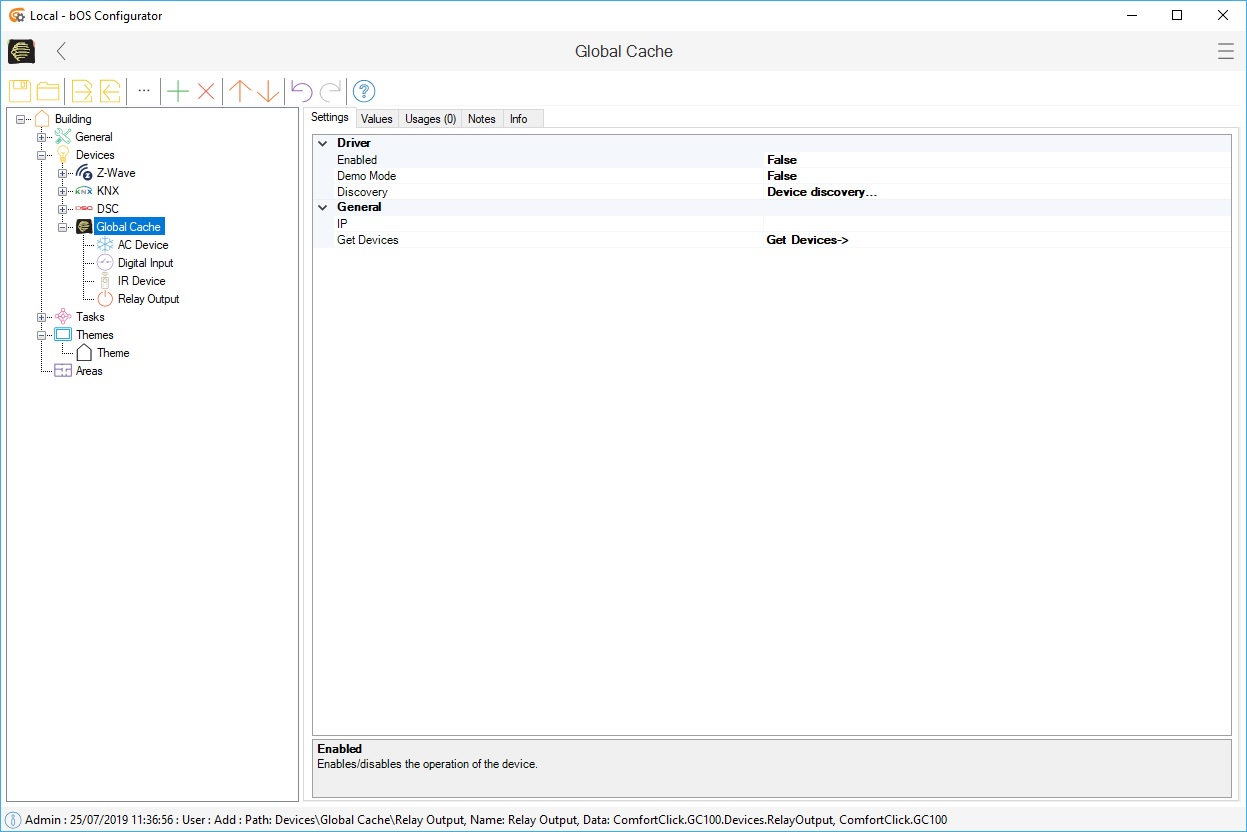
Picture 1: Global cache node
Discovery function can be used to scan, identify and connect to the correct Global Cache device. Once the device is discovered, device’s IP will be automatically inserted. After the device is connected to the bOS, Get devices function can be used to discover and display the devices that are connected and linked to the Global Cache device.
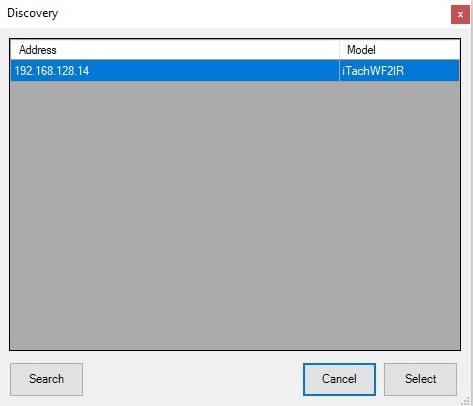
Picture 2: Global Cache discovery
Before creating the bOS configuration configure the Global Cache device according to the manufacturer's instructions. Network adapter and machine running bOS Server should both be using the same network in order to be able to communicate with each other.
Global Cache nodes supports the following subnodes:
AC Device: used for controlling an AC device via IR emitters connected to the GC-100 network adapter.
Digital Input: used for reading a digital input state.
IR Device: used for controlling a device via IR emitters connected to GC-100 network adapter.
Relay Output: used for controlling a relay output.
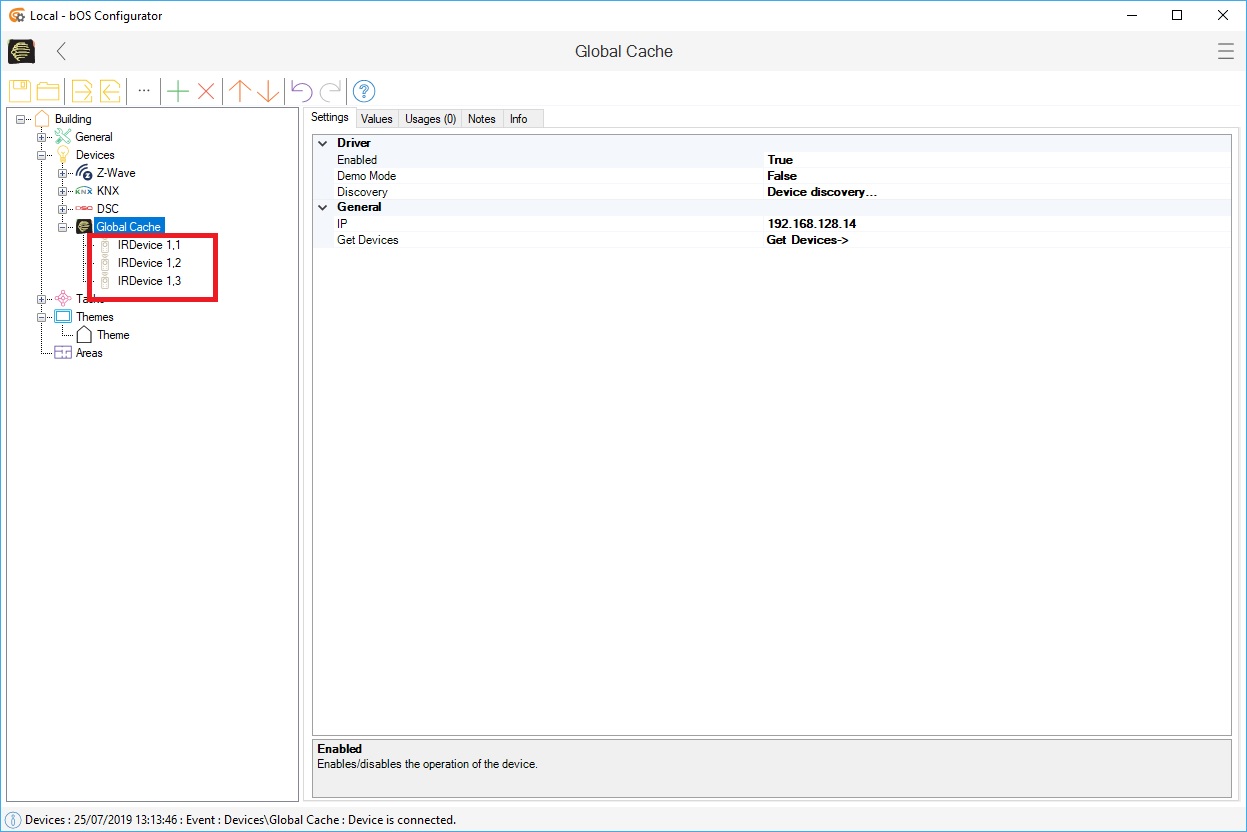
Picture 3: Global Cache device list
Module and Relay settings
Each subnode has Module and Relay settings which define the input/output of the device according to the device type:
- GC100-12, GC100-18, GC100-18R

GC100-6,
iTach WF2IR, IP2IR, IP2IR-P, WF2CC, IP2CC, IP2CC-P,
iTach Flex
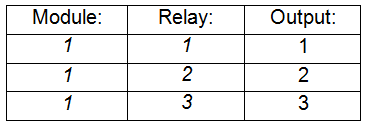
Importing and learning IR codes
IR codes for most of the devices can be imported from the database by clicking on the device and Import database button.
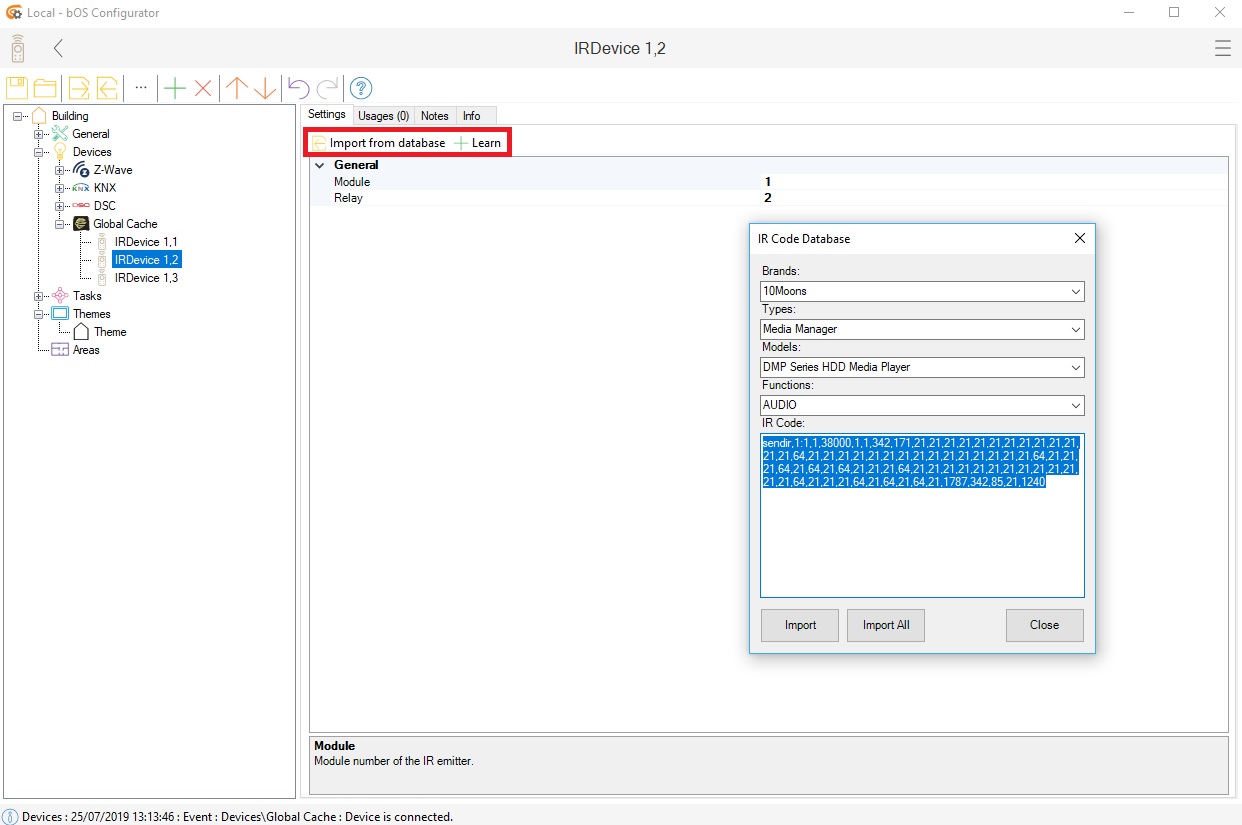
Picture 4: Import button
IR codes can be learned with GC-IRL device or with ItachFlex. All IR codes can be entered in HEX (Philips Pronto) or GC-IRL (Global Cache IR Learner) format. You can also learn the commands through bOS Configurator with the use of the Learn IR Code in IR device node settings. By clicking on the learn button the IR learning connection form is displayed.
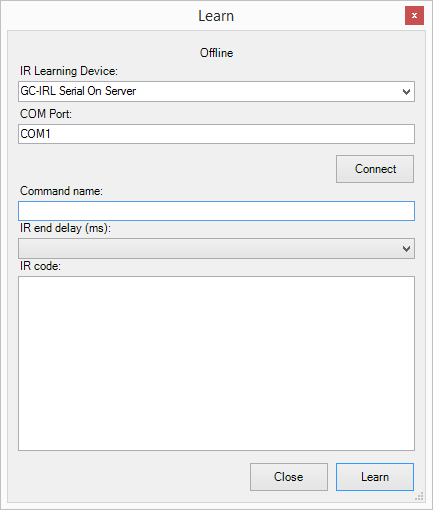
Picture 5: IR learning form
IR end delay specifies the delay in ms for an end of a command. Shorter end delays produce shorter codes. Some experimenting is needed to get a suitable end delay for a particular device.
Command name text box should be filled and the button on the IR remote should be pressed. The learned code is displayed in the IR code text box. By clicking on the Learn button, the command will be inserted into the command list. Additional commands can be learned if necessary. By clicking on the close button learned commands will be added to the configuration.
Alternatively you can use the iLearn Software for learning IR codes and use copy paste to insert commands into bOS. Before using the GC-IRL command, the GC-IRL string should be stripped so that it begins with the frequency parameter.
IR Device
IR Device node represents the device controlled by the Global Cache. Under IR Device node multiple commands and states can be added.
Digital Input
Digital Input node reads the state of the digital input. Digital inputs can be used instead of the IR emitters. The inputs should be enabled through the device's web interface. For iTach devices digital inputs are read with the UDP protocol. The appropriate port should be entered.
Relay Output
Relay Output node sets the state of the digital output (contact closure). Digital inputs can be used instead of the IR emitters. The inputs should be enabled through the device's web interface. For iTach devices digital inputs are read with the UDP protocol. The appropriate port should be entered in the node settings.
AC Device
AC Device node represents virtual states of an Air Conditioner device.
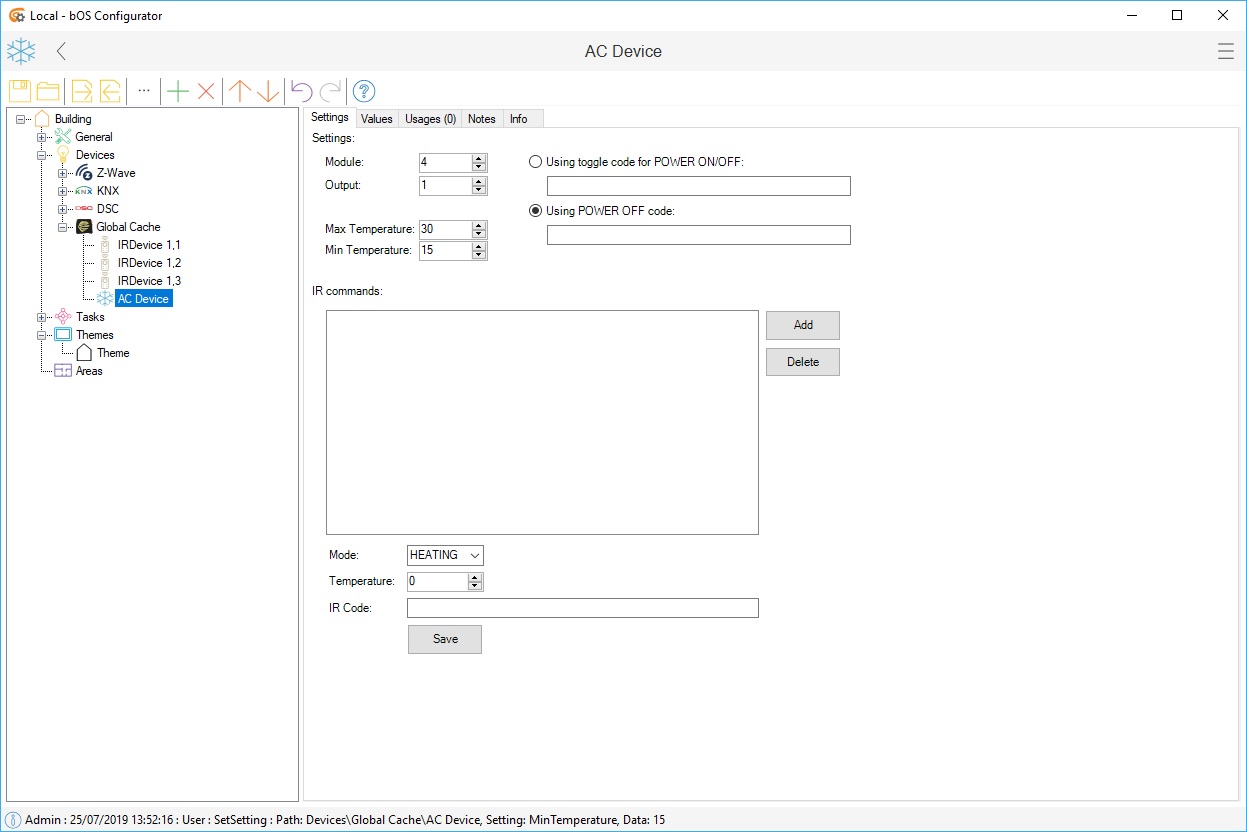
Picture 6: AC unit device form


